Neuronal Lipophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Mechanisms, Dual Roles, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets
Keywords:
- Neuronal lipophagy, neurodegenerative diseases, lipid metabolism, autophagy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, TFEB, mitochondrial dysfunction, ferroptosis, nanotherapy, lifestyle interventions, omics, CNS biomarkers.
Abstract
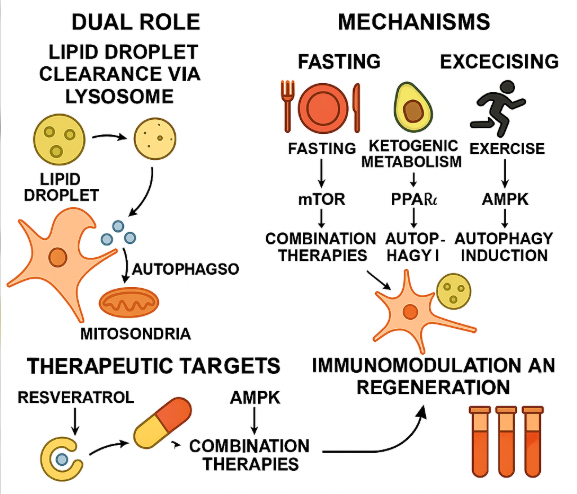
Neuronal lipophagya specialized form of autophagy targeting lipid droplets for lysosomal degradationhas emerged as a critical regulator of lipid metabolism, redox balance, and mitochondrial function in the central nervous system (CNS). This review comprehensively explores the molecular mechanisms governing neuronal lipophagy and its dual role in the pathogenesis and protection against major neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Huntington’s disease (HD). Impaired lipophagic flux has been implicated in lipid droplet accumulation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction, while excessive activation may lead to lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. We examine key regulatory pathwayssuch as TFEB, Rab proteins, LAMP2A, and FOXO transcription factorsand their disease-specific disruptions. Furthermore, we discuss emerging therapeutic strategies including pharmacological agents (resveratrol, metformin, trehalose), gene editing, miRNA modulation, and nanotechnology-based delivery systems. Lifestyle interventions like intermittent fasting, ketogenic diets, and exercise are also evaluated for their capacity to induce neuroprotective lipophagy. Finally, we highlight future directions involving single-cell omics, biomarker discovery, and combinatorial therapies aimed at translating lipophagy modulation into clinical neurotherapeutics. Understanding and harnessing neuronal lipophagy offers a promising frontier for combating the rising burden of neurodegenerative diseases.