Effectiveness of Core Stabilization Exercises in Reducing Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized Control Trial
Keywords:
- Chronic low back pain, Core stabilization exercises, Physiotherapy, Visual Analog Scale, Oswestry Disability Index, Randomized controlled trial, Functional disability, Pain management
Abstract
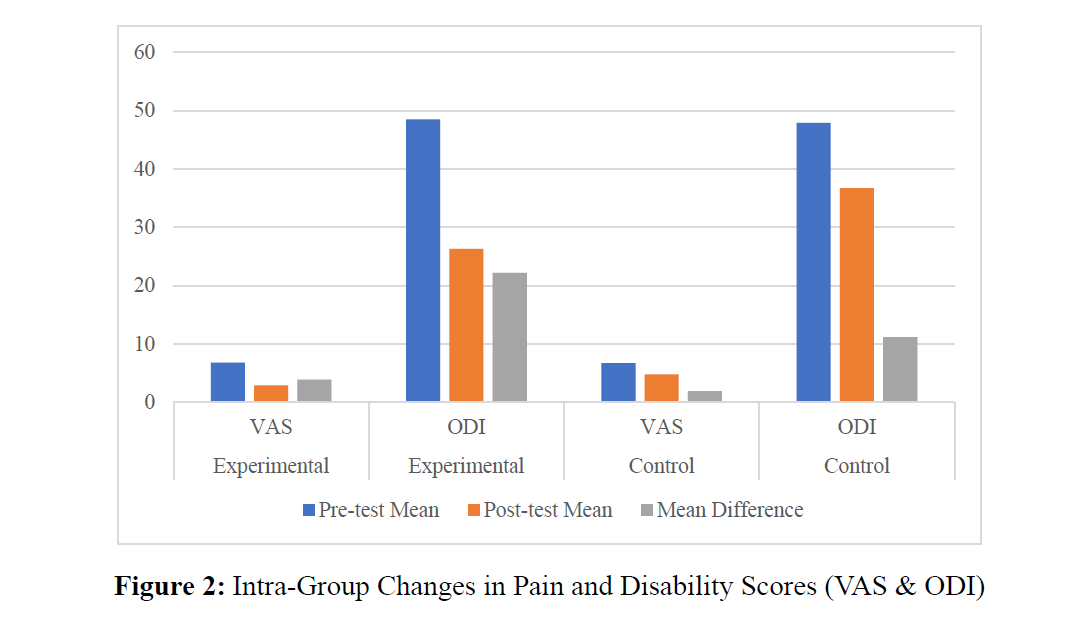
This randomised control study was aimed at determining whether core stabilisation exercises were superior than conventional physiotherapy for alleviation of CLBP. Sixty non-specific CLBP volunteers (aged 25-50) were randomised to undergo core stabilisation exercises (experimental group) and conventional physiotherapy (control group), for 6 weeks intervention. We used Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) to grade the intensity of pain and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) to grade functional disability. The experimental group showed significant improvement in impairment and pain post intervention as indicated by VAS rating and ODI score improvement of 57.35% and 45.76% respectively as compared to control group improvement of 28.36% and 23.38% respectively. There was also more satisfaction among participants in the experimental group. The outcome is in line with the actual medical practice, as the basic principles of core stabilisation exercises prescribed as the main therapy option are found to provide better results than standard physiotherapy in the treatment of chronic low back pain and improvement of functions.